Skin cysts are typically benign, fluid-filled sacs. Common types include epidermoid, pilar, sebaceous, and ganglion cysts. Seek medical advice if cysts grow, become painful, or show signs of infection.
- Dr Sharon Crichlow
- Reading Time: 10 Mins
“I’ve found a lump on my head. What could it be?” This common worry brings many people to search for answers. Finding an unusual bump on your skin can be concerning, but most skin cysts are harmless. In this visual guide, we’ll help you identify different types of cysts and understand when you should seek medical advice.
Key Takeaways
- Most skin cysts are harmless and non-cancerous, though they may require medical evaluation if they grow, become painful, or show signs of infection.
- Different cyst types appear in specific body areas: epidermoid cysts on face and back, pilar cysts on scalp, and ganglion cysts near joints.
- Professional removal is recommended over attempting to pop cysts yourself, which can lead to infection, scarring, and recurrence.
Table of Contents
What Are Cysts on the Skin?
Skin cysts are closed sac-like structures that develop within or under the skin. They contain fluid, semi-solid, or gaseous material and are usually slow-growing and painless.
Unlike warts (which are caused by viral infections) or skin tags (which are small flesh-coloured growths), cysts are enclosed within a membrane and typically contain specific materials like keratin, sebum, or fluid.
Cysts also differ from lipomas, which are fatty lumps that develop between the skin and muscle layers. While both are usually harmless, they have different appearances and treatments.
Cysts Under the Skin vs Cysts on the Skin
Cysts present differently depending on whether they develop under or on the skin surface.
Cysts under the skin typically appear as firm, smooth lumps that move slightly when pressed. They develop in deeper skin layers or subcutaneous tissue. These cysts often feel like a small ball beneath the skin and may grow larger over time.
Cysts on the skin form closer to the surface and may have a visible opening (sometimes called a punctum). They might appear as dome-shaped bumps and occasionally discharge material if pressed.
| Feature | Cysts Under Skin | Cysts On Skin |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Smooth, rounded bump | Dome-shaped with a possible visible opening |
| Feel | Firm, mobile lump | Softer, less mobile |
| Visibility | Less defined borders | More clearly defined |
| Common Types | Sebaceous cysts, lipomas | Epidermoid cysts, milia |
Most Common Types of Skin Cysts (With Pictures)
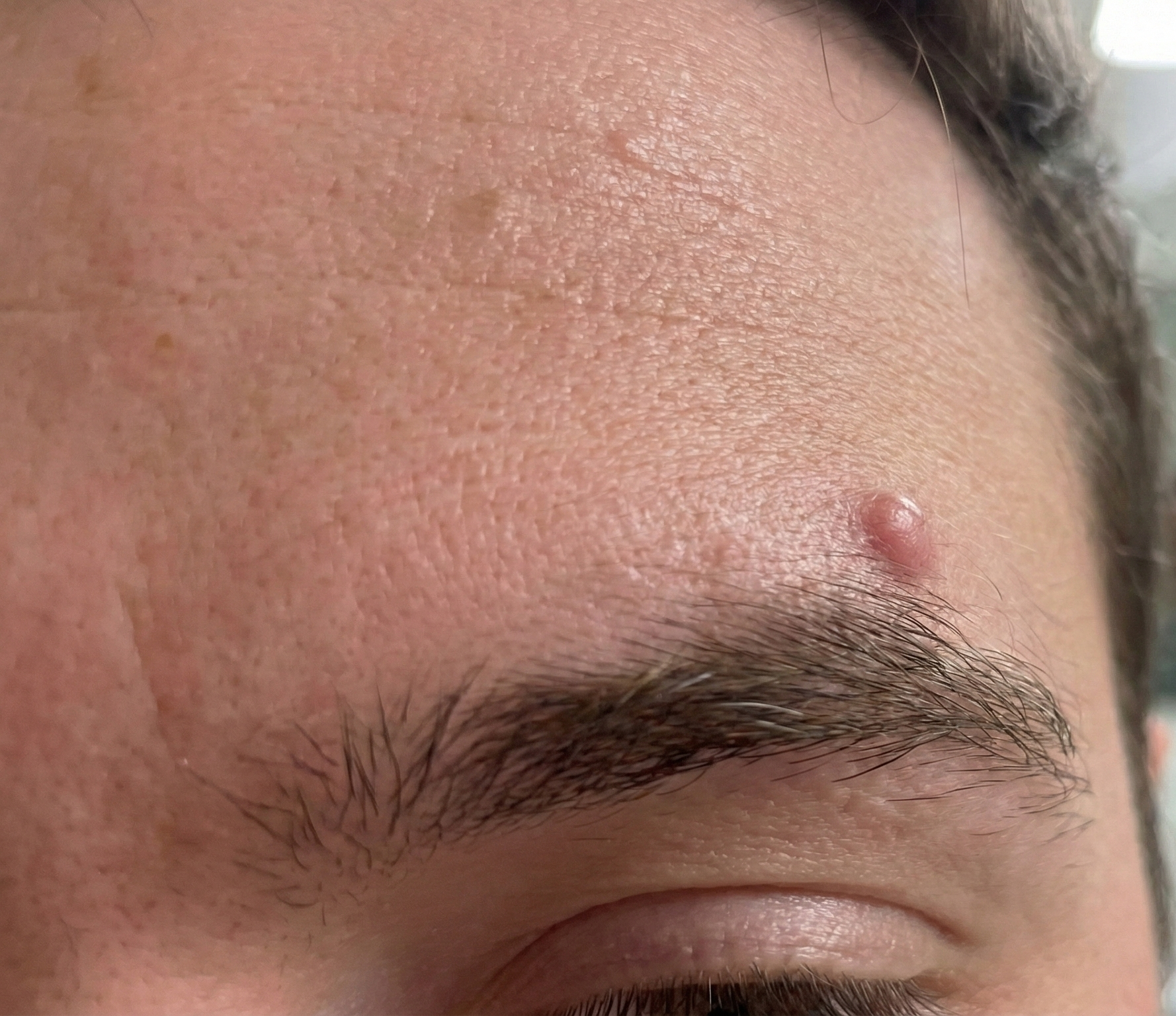
Epidermoid (Epidermal) Cysts
A small, solid lump that forms beneath the skin when surface skin cells become trapped. These cysts commonly appear on the face, neck, or torso and may show a tiny central opening.
Epidermoid cysts are the most common skin cysts, accounting for 74.3% of benign skin cysts according to a comprehensive study of 1,160 cases.
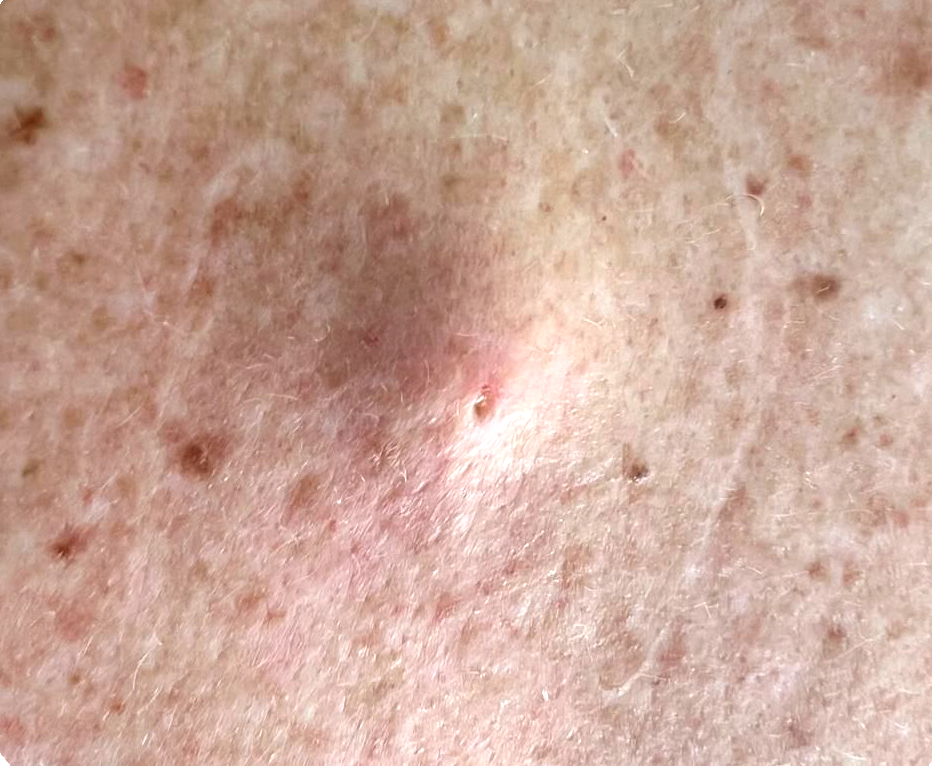
- Appearance: Round, firm bumps that are skin-colored or slightly yellow. They typically have a small, dark punctum (opening) at the centre.
- Common locations: Face, neck, back, and chest
- Size: Usually between 0.5 and 4 cm in diameter
- Causes: They form when skin cells that should be shed instead move deeper into the skin and multiply. These cells form a sac and secrete keratin, creating the cyst.
For treatment options for epidermoid cysts on the forehead, our forehead cyst removal service offers minimally invasive solutions.
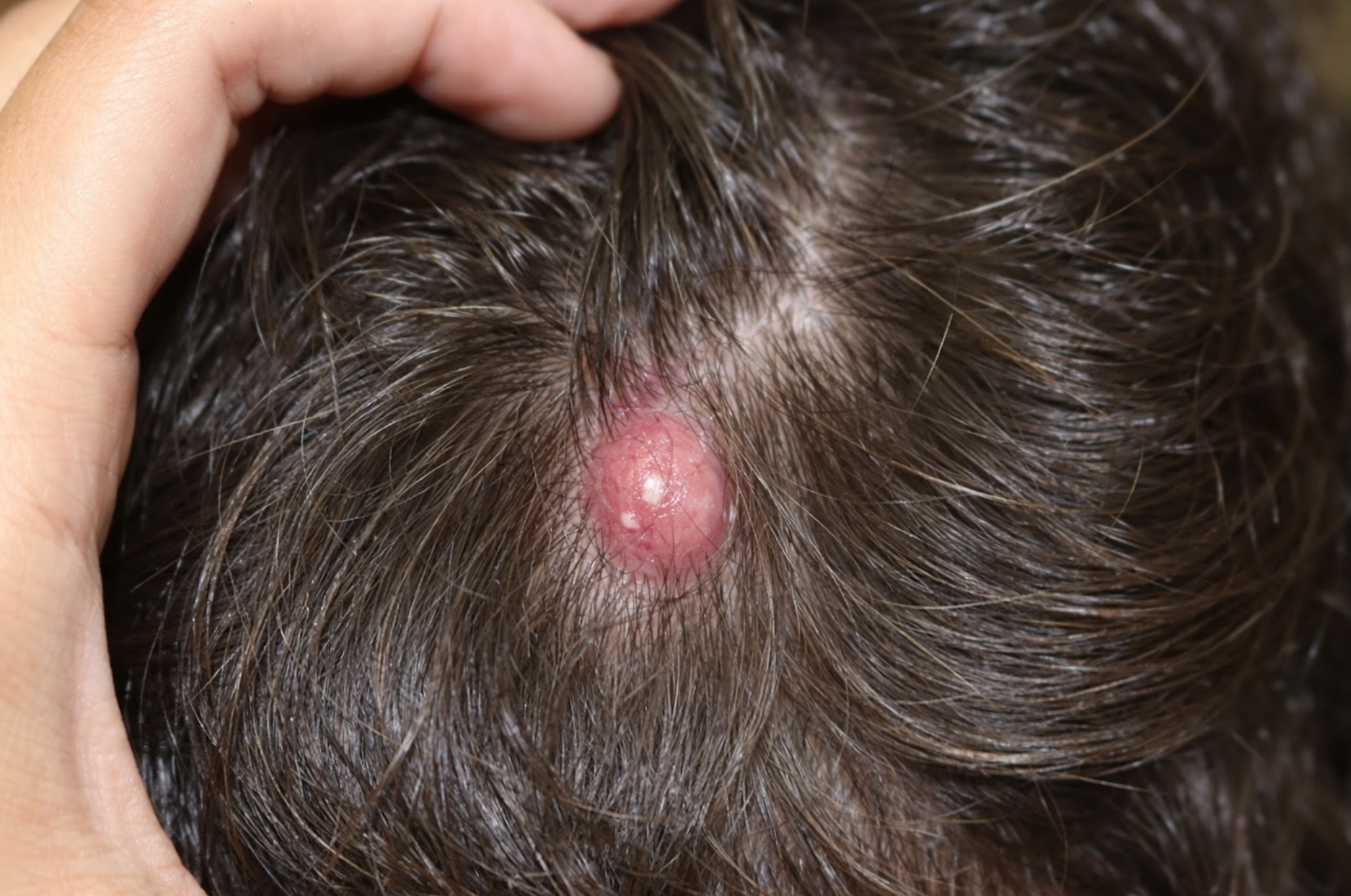
Pilar (Trichilemmal) Cysts
A smooth, dome-shaped lump that develops from a hair follicle, most frequently on the scalp. These cysts are usually firm, painless, and may sometimes occur in more than one area.
Pilar cysts account for about 15% of all cutaneous cysts according to recent studies. Unlike epidermoid cysts, they don’t usually have a visible central pore or opening.
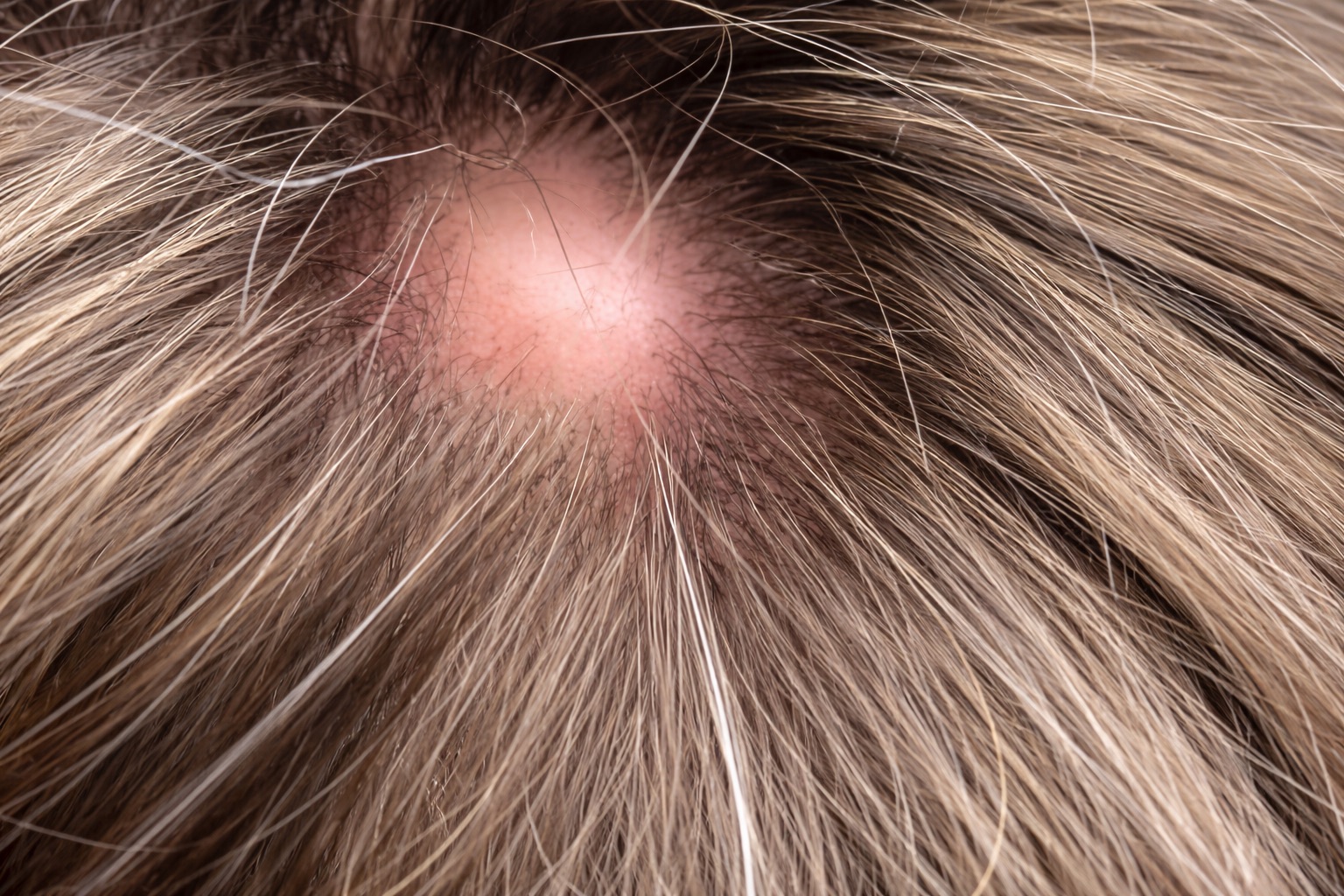
- Appearance: Smooth, round, firm bumps without a visible central pore. They're typically flesh-colored.
- Common locations: Scalp (over 90% occur here)
- Size: Usually 0.5-5 cm in diameter
- Causes: They develop from hair follicles, specifically from the outer root sheath of the hair follicle.
If you're concerned about a pilar cyst, our specialist pilar cyst removal services can help.
Sebaceous Cysts
A rounded swelling caused by a blocked oil gland, containing a thick, yellowish substance. They can develop anywhere on the skin and may feel soft, firm, or mildly tender to touch.
Though commonly referred to, true sebaceous cysts are relatively rare. Many cysts labelled “sebaceous” are actually epidermoid cysts.
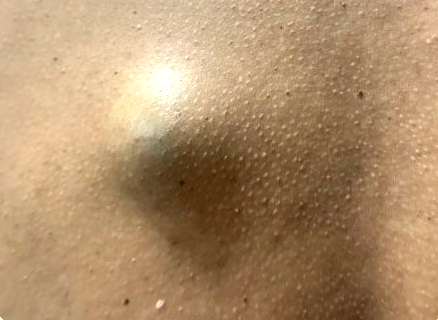
- Appearance: Yellow or flesh-colored bumps that may have a slight odour when ruptured.
- Common locations: Face, neck, back
- Size: Typically 1-4 cm in diameter
- Causes: They form from blocked sebaceous glands, which normally produce oil for your skin and hair.
For professional treatment of sebaceous cysts, consider our cyst removal treatment.
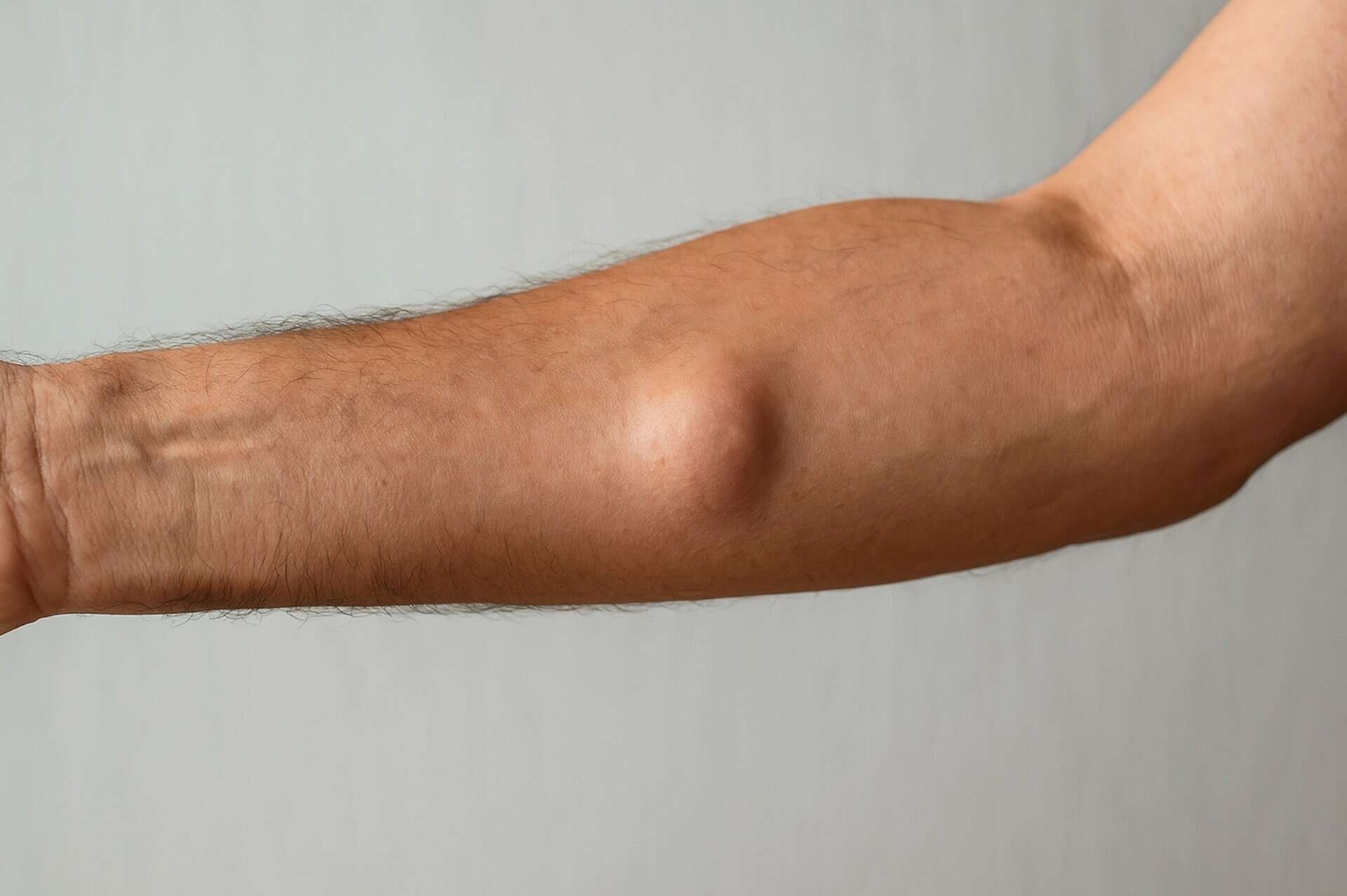
Ganglion Cysts
A firm, smooth swelling that forms near a joint or tendon, most commonly around the wrist. It contains a clear, jelly-like fluid and may increase or decrease in size over time.
Ganglion cysts form in relation to joints or tendons.
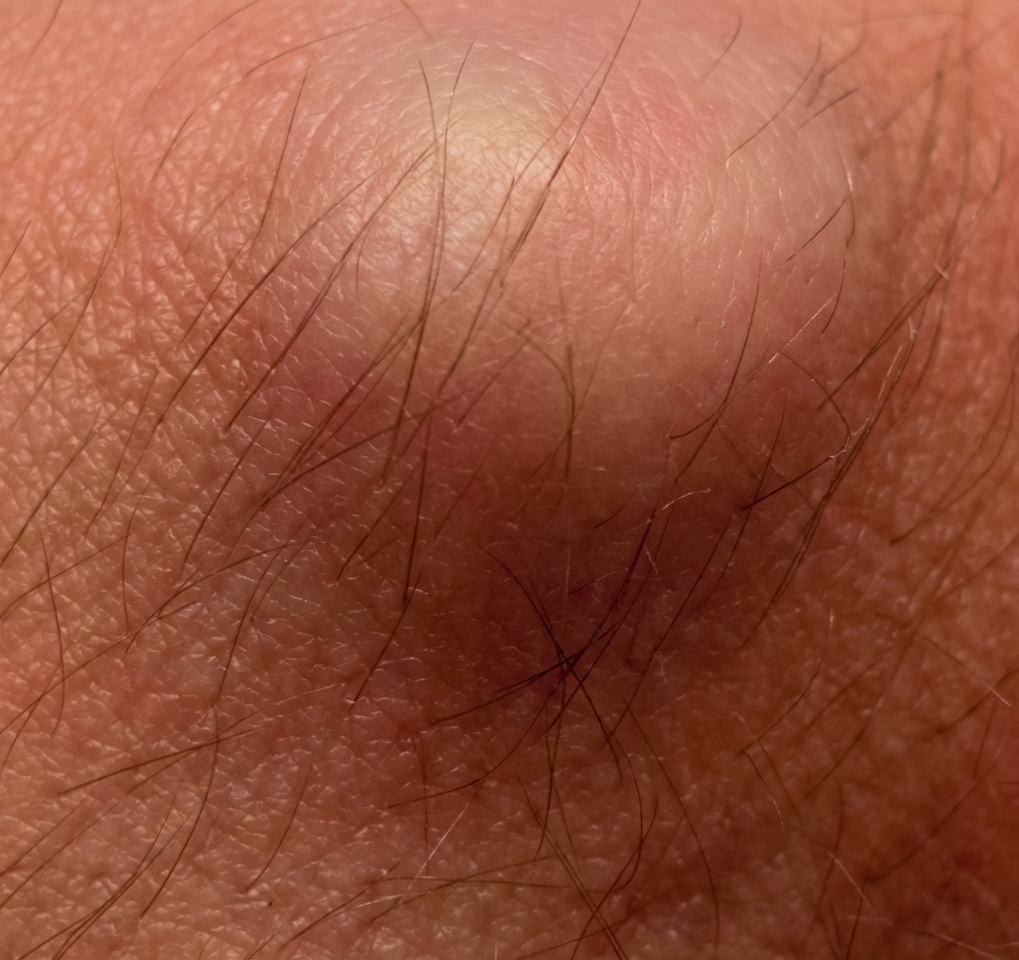
- Appearance: Round, firm, smooth lumps that may be painful when pressed.
- Common locations: Wrists, hands, ankles, and feet
- Size: Can range from pea-sized to 2.5 cm
- Causes: They develop from joint or tendon sheaths and contain synovial fluid.
Other Types of Skin Cysts
| Cyst Type | Appearance | Common Locations | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Milia | Tiny white or yellowish bumps | Face, especially around eyes | Small (1–2 mm), resemble whiteheads |
| Dermoid cysts | Firm, slow-growing nodules | Face, neck, scalp | Present at birth; may contain hair or skin glands |
| Mucous cysts | Clear, fluid-filled bumps | Lips, inside the mouth | Soft, painless; may burst and recur |
| Breast cysts | Smooth, round lumps | Breast tissue | May be tender, especially before periods |
| Hidrocystomas | Dome-shaped, translucent | Near the eyes, face | Contain clear fluid; may have a bluish tinge |
Where Do Skin Cysts Commonly Appear?
Cysts can develop almost anywhere on the body, but certain types favour specific locations:
- Head and neck region: Common sites for epidermoid cysts, pilar cysts, and dermoid cysts. If you’ve found a lump on your head, it’s likely a pilar cyst. Eyelid cysts are typically chalazia or hidrocystomas.
- Trunk: The back is the most common location for epidermoid cysts.
- Extremities: Ganglion cysts typically occur on wrists, hands, ankles, and feet.
The location can often help identify the type of cyst. For example, a round, smooth bump on the scalp is most likely a pilar cyst, while a similar bump on the wrist might be a ganglion cyst.
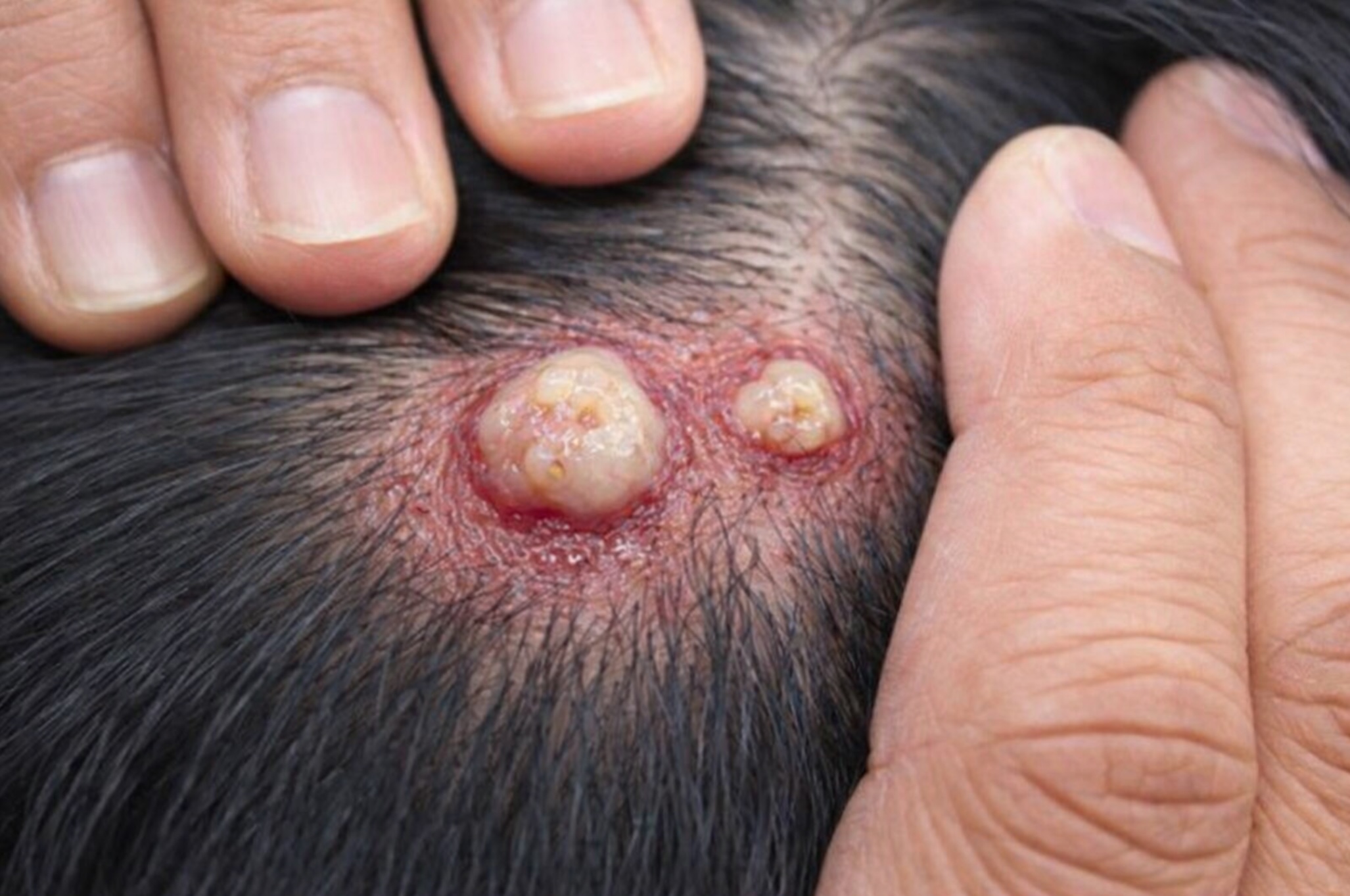
What Do Infected or Inflamed Cysts Look Like?
Infected cysts present distinctive signs that distinguish them from their benign counterparts:
- Redness and warmth around the cyst
- Increased tenderness or pain
- Swelling beyond the cyst’s normal boundaries
- Discharge of pus or foul-smelling material
- Fever (in severe cases)
An infected cyst requires prompt medical attention to prevent complications such as cellulitis or abscess formation.
When Should You See a Doctor?
While most skin cysts are harmless, certain situations warrant professional assessment.

Professional evaluation ensures proper diagnosis and treatment, especially since some more serious conditions can initially resemble common cysts.
How Are Skin Cysts Diagnosed and Treated?
Diagnosis typically involves physical examination by a healthcare professional. In some cases, ultrasound imaging or a biopsy might be necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment options include:
- Observation: Small, asymptomatic cysts may require no treatment
- Injection: Corticosteroid injections can reduce inflammation
- Incision and drainage: Releasing the contents of infected cysts
- Complete surgical removal: Excising the entire cyst wall to prevent recurrence
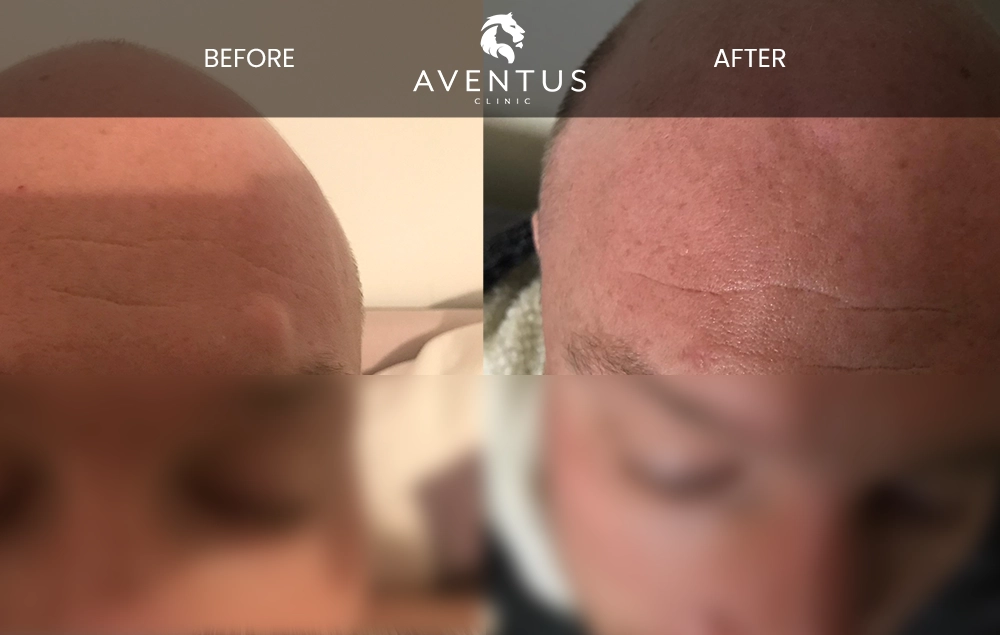
At Aventus Clinic, our cyst removal treatment offers professional care with minimal scarring.
Conclusion
While most cysts are harmless, proper evaluation ensures appropriate treatment.
If you’re concerned about a cyst, our team of specialists can provide expert assessment and treatment options tailored to your needs. We offer same-day procedures with minimal scarring and quick recovery times.
Book your free cyst assessment today to take the first step toward effective, professional care.
FAQs
Are skin cysts dangerous?
Most skin cysts are benign and pose no health risk. However, very rarely, some cysts may develop malignant changes. This is why unusual or changing cysts should be examined by a healthcare professional.
Can cysts go away on their own?
Some smaller cysts may disappear without treatment. However, most established cysts won’t resolve spontaneously and may gradually enlarge over time.
Do cysts hurt?
Most cysts are painless unless they become infected, inflamed, or press on nearby nerves. Pain is often a sign that medical attention is needed.
Are cysts cancerous?
The vast majority of skin cysts are non-cancerous. However, any growth that changes rapidly, bleeds, or doesn’t heal should be evaluated professionally to rule out more serious conditions.
What’s the difference between a cyst and a tumour?
Cysts are fluid-filled sacs, while tumours are solid masses of tissue. While most cysts are benign, tumours can be either benign or malignant. A healthcare professional can determine the difference.
Can you pop a cyst?
You should never attempt to pop or drain a cyst yourself. This can lead to infection, inflammation, and scarring. Professional medical treatment is always the safer option.

Found a lump or cyst on your skin? Our dermatology specialists can assess your concern with a free online consultation.




 WHATSAPP
WHATSAPP